Welcome to our in-depth exploration of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a common yet complex health condition affecting many individuals worldwide. PCOS is characterized by hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual cycles, and the formation of small cysts on the ovaries. It can manifest in various ways and impact different aspects of a person’s life, from fertility to overall well-being. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of PCOS and medicine for polycystic ovaries to help you better understand and manage this condition.
Contents
What Is PCOS?
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects individuals, primarily women, during their reproductive years. The condition is characterized by a range of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone, and the development of small fluid-filled sacs or cysts on the ovaries. These cysts may interfere with the regular release of eggs during the menstrual cycle, contributing to fertility challenges.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects individuals, primarily women, during their reproductive years. The condition is characterized by a range of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone, and the development of small fluid-filled sacs or cysts on the ovaries. These cysts may interfere with the regular release of eggs during the menstrual cycle, contributing to fertility challenges.
PCOS often presents with a diverse set of symptoms, making it a complex and individualized condition. Beyond reproductive issues, individuals with PCOS may experience other challenges such as acne, weight gain, and increased risk of metabolic disorders. The syndrome requires a multidimensional approach to management.
When To Consider Medicine For Polycystic Ovaries?
The decision to consider medicine for Polycystic Ovaries is typically based on the specific symptoms and goals of the individual, as well as guidance from healthcare professionals. Medications may be recommended in various scenarios, including:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles
If PCOS is causing irregular or absent menstrual periods, medications may be prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia.
- Fertility Concerns
For individuals experiencing difficulty getting pregnant due to PCOS-related issues, fertility medications may be considered to induce ovulation and improve the chances of conception.
- Androgen-Related Symptoms
Medications such as anti-androgens may be prescribed to address symptoms related to elevated androgen levels, including acne and hirsutism (excessive hair growth).
- Insulin Resistance
For individuals with PCOS and insulin resistance, medications may be recommended. Metformin helps to improve insulin sensitivity and can assist in managing symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles and weight gain.
It’s important to note that medication is just one component of PCOS management, and lifestyle modifications often play a crucial role. The decision to use medication should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider. They can assess individual circumstances, consider potential risks and benefits, and tailor the treatment plan to the specific needs and goals of the person with PCOS.
What Are Some Examples of Medicine For Polycystic Ovaries?
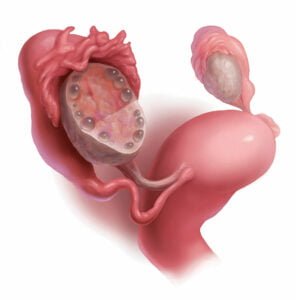 Several medications may be used to manage various symptoms associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). It’s important to note that the choice of medication depends on the specific symptoms and goals of the individual. Here are some examples of medications for polycystic ovaries:
Several medications may be used to manage various symptoms associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). It’s important to note that the choice of medication depends on the specific symptoms and goals of the individual. Here are some examples of medications for polycystic ovaries:
Birth Control Pills (Oral Contraceptives)
Birth control pills are frequently prescribed to individuals with PCOS, particularly those experiencing irregular menstrual cycles. These pills contain a combination of estrogen and progestin, hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle by suppressing ovulation. By preventing the ovaries from releasing eggs, birth control pills help establish a more predictable and regular menstrual cycle.
Anti-Androgens
For individuals with PCOS dealing with symptoms related to elevated androgen levels, such as acne and hirsutism, anti-androgen medications like spironolactone may be prescribed. Spironolactone works by blocking the effects of androgens on the skin and hair follicles, leading to a reduction in acne and the growth of excess facial or body hair. It is important to note that these medications are typically used in combination with other treatments and should be administered under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Metformin
Metformin is commonly prescribed for individuals with PCOS who exhibit insulin resistance or have elevated insulin levels. This medication improves insulin sensitivity, helping the body use insulin more effectively. By addressing insulin resistance, metformin can contribute to better regulation of menstrual cycles and assist in managing weight. It may be particularly beneficial for individuals with PCOS who are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Fertility Medications
Women with PCOS facing challenges with ovulation and fertility may be prescribed fertility medications such as clomiphene citrate or letrozole. These medications stimulate the ovaries to release eggs, increasing the chances of conception. They are often used in combination with careful monitoring of the menstrual cycle to optimize timing for conception. Fertility medications are an important component of assisted reproductive technologies and can be instrumental in helping individuals with PCOS achieve pregnancy.
Gonadotropins
In more complex cases of infertility associated with PCOS, gonadotropins may be recommended as a fertility treatment. Gonadotropins are hormones that include follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Unlike oral medications such as clomiphene citrate or letrozole. This stimulates the ovaries indirectly, gonadotropins are administered through injections and directly stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. However, the use of gonadotropins requires careful monitoring, as there is an increased risk of multiple pregnancies and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
Insulin Sensitizers
In addition to metformin, other insulin-sensitizing medications, such as thiazolidinediones (TZDs), may be considered in the management of PCOS. TZDs, like pioglitazone, improve insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues, helping to reduce insulin resistance. By addressing insulin resistance, these medications can contribute to better metabolic health and may have positive effects on symptoms related to PCOS, such as irregular menstrual cycles. However, their use is often carefully monitored due to potential side effects.
It’s crucial to emphasize that the choice of medicine for polycystic ovaries should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider. The specific symptoms, overall health, and reproductive goals of the individual will influence the selection of medications. Regular follow-up with a healthcare professional will help to monitor the effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
Can Pills Cure Polycystic Ovaries?
 While there is currently no cure for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), medication, including oral contraceptives (birth control pills), can effectively manage and alleviate some of its symptoms. Birth control pills are commonly prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, and alleviate symptoms such as acne and excess hair growth associated with elevated androgen levels.
While there is currently no cure for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), medication, including oral contraceptives (birth control pills), can effectively manage and alleviate some of its symptoms. Birth control pills are commonly prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, and alleviate symptoms such as acne and excess hair growth associated with elevated androgen levels.
By preventing ovulation and stabilizing hormonal imbalances, these pills contribute to a more predictable menstrual cycle and address some of the manifestations of PCOS. However, it’s important to note that the discontinuation of birth control pills may result in the return of irregular menstrual cycles and associated symptoms.
Medication plays a valuable role in symptom management. Still, a comprehensive approach to PCOS often involves lifestyle modifications alongside medical interventions. Those with PCOS need to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor a treatment plan that addresses their specific symptoms and goals.
What Are The Advantages of Medicine For PCOS?
Medicine for Polycystic Ovaries offer several advantages in managing the condition and its associated symptoms:
- Regulation of Menstrual Cycles: Birth control pills, a common medication for PCOS, help regulate menstrual cycles. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with irregular or absent periods, reducing the risk of endometrial hyperplasia (overgrowth of the uterine lining) and associated health concerns.
- Symptom Management: Medications can effectively address symptoms related to elevated androgen levels. This includes the reduction of acne and excess hair growth (hirsutism), improving the quality of life for individuals with PCOS.
- Improved Fertility: Fertility medications stimulate ovulation, increasing the chances of conception for individuals struggling with infertility due to PCOS. These medications provide valuable options for those seeking to build a family.
- Management of Hormonal Imbalances: Medications can help normalize hormone levels in individuals with PCOS, contributing to a better balance of estrogen, progesterone, and androgens. This can alleviate various symptoms and improve overall hormonal health.
- Reduced Risk of Endometrial Cancer: By regulating menstrual cycles and reducing the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, certain medications, such as birth control pills, may help lower the long-term risk of endometrial cancer in individuals with PCOS.
- Individualized Treatment: Medications can be tailored to the specific symptoms and goals of each individual with PCOS, allowing for a personalized approach to treatment. This individualization is crucial given the varied presentations of PCOS among different individuals.
It’s important to note that while medications offer significant advantages in managing PCOS, they are often most effective when used in conjunction with lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise. Additionally, any medication regimen should be discussed with and supervised by a healthcare professional to ensure safety and optimal effectiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) involves understanding its complexities and adopting a multifaceted approach to care. While there’s no cure for PCOS, medications like birth control pills, anti-androgens, and fertility treatments can effectively manage symptoms, regulate menstrual cycles, and enhance fertility. These medications, along with lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, empower individuals to take control of their health.
It’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to create a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and goals. By combining medical interventions with a holistic approach, individuals with PCOS can enhance their quality of life and manage the condition for long-term well-being. If you are facing PCOS related issues, pcos treatment at HerMantra can help. Book your free trial online pcos treatment session now.


