Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) are two commonly encountered endocrine disorders affecting women of reproductive age. These conditions not only pose fertility challenges but also bring with them a range of metabolic and hormonal imbalances. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into effective strategies of treatment for PCOD and PCOS, aiming to provide women with valuable insights and options for managing these conditions.
Contents
Defining PCOD and PCOS
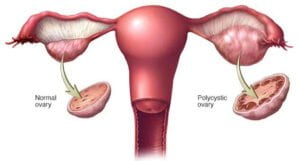
PCOD:
Polycystic Ovary Disorder is characterized by the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries. These cysts are small, fluid-filled sacs, which can lead to an enlarged ovary. PCOD is often associated with irregular menstrual cycles and hormonal imbalances, contributing to difficulties in conceiving.
PCOS:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a broader term encompassing not only ovarian cysts but a spectrum of symptoms related to hormonal dysregulation. In addition to menstrual irregularities and fertility issues, PCOS is marked by elevated levels of androgens, the male hormones, leading to a variety of symptoms like acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and alopecia.
When Do I Need Treatment for PCOD and PCOS?
Determining when to seek treatment for Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) depends on various factors and individual experiences. Here are key indicators that may suggest the need for treatment:
Menstrual Irregularities:
- Absence of Menstrual Periods (Amenorrhea): Infrequent or absent menstrual periods may indicate irregular ovulation, necessitating attention for overall reproductive health.
- Heavy or Prolonged Menstrual Bleeding: Excessive or prolonged bleeding can lead to anemia and may require treatment to regulate and normalize menstrual flow.
Fertility Concerns:
- Difficulty Conceiving: Challenges in conceiving due to irregular ovulation may prompt consultation with a fertility specialist.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): If fertility issues persist, interventions like in vitro fertilization (IVF) or ovulation-inducing medications may be considered.
Hormonal Imbalances:
- Symptoms of Androgen Excess: Physical manifestations such as acne, hirsutism, and alopecia due to elevated androgen levels may impact quality of life, prompting consideration for medical management.
- Insulin Resistance: Addressing insulin resistance, common in PCOD/PCOS, through lifestyle changes or medications may be necessary.
Psychological and Emotional Well-being:
- Impact on Mental Health: PCOD/PCOS can contribute to anxiety, depression, and body image issues, necessitating treatment, including counseling and support groups.
Different Treatment for PCOD and PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are related conditions with overlapping symptoms, but the treatment approach may vary based on individual needs and goals. Here are different treatments commonly considered for managing PCOD and PCOS:
Lifestyle Modifications

Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Adopting healthy habits can positively impact hormonal balance, improve insulin sensitivity, and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions. Here are key lifestyle modifications often recommended for individuals with PCOD and PCOS:
1. Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is a cornerstone of PCOD/PCOS management. Even a modest weight loss can lead to improvements in hormonal balance and menstrual regularity.
2. Balanced Diet:
- Whole Foods: Focus on a diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Minimize the consumption of processed and sugary foods.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Opt for complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index to help regulate blood sugar levels. Examples include whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables.
3. Regular Exercise:
- Aerobic Exercise: Engage in regular aerobic exercises such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle mass, improve metabolism, and enhance insulin sensitivity.
4. Stress Management:
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises to lower cortisol levels and improve overall well-being.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get sufficient and quality sleep each night. Lack of sleep can contribute to hormonal imbalances and insulin resistance.
5. Hydration:
- Water Intake: Stay adequately hydrated by consuming an ample amount of water throughout the day. Proper hydration supports overall health and may aid in weight management.
6. Limiting Caffeine and Alcohol:
- Caffeine Intake: Moderate caffeine consumption, as excessive caffeine can contribute to stress and disrupt hormonal balance.
- Alcohol Consumption: Consume alcohol in moderation, as excessive alcohol intake can affect liver function and exacerbate hormonal imbalances.
7. Quit Smoking:
- Smoking Cessation: Quit smoking if applicable, as smoking can contribute to various health issues, including hormonal imbalances.
8. Regular Health Check-ups:
- Medical Monitoring: Regularly monitor and manage other health conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, which may coexist with PCOD/PCOS.
Medications

Medications are often an integral part of the treatment plan for individuals with Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). These medications aim to address specific symptoms, regulate menstrual cycles, and manage hormonal imbalances associated with these conditions.
Here are some common medications used in the management of PCOD and PCOS:
1. Oral Contraceptives (Birth Control Pills):
- Purpose: Regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels.
- Mechanism: Combines estrogen and progestin to inhibit ovulation, regulate menstrual cycles, and reduce symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
2. Anti-Androgen Medications:
- Spironolactone:
- Purpose: Reduces androgen levels, addressing symptoms like hirsutism and acne.
- Mechanism: Acts as an anti-androgen by blocking the effects of androgens on the skin and hair follicles.
3. Insulin-Sensitizing Medications:
- Metformin:
- Purpose: Improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate menstrual cycles.
- Mechanism: Reduces insulin resistance, lowers blood sugar levels, and addresses metabolic aspects of PCOD/PCOS.
4. Ovulation-Inducing Medications:
- Clomiphene Citrate and Letrozole:
- Purpose: Induces ovulation in women trying to conceive.
- Mechanism: Stimulates the release of hormones necessary for ovulation, increasing the chances of pregnancy.
Surgical Interventions
Fertility treatments play a crucial role for individuals with Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) who may experience challenges in conceiving due to irregular ovulation. These treatments aim to induce or enhance ovulation, increase the chances of successful conception, and support a healthy pregnancy. Here are common fertility treatments for individuals with PCOD/PCOS:
1. Ovulation-Inducing Medications:
- Clomiphene Citrate:
- Purpose: Stimulates the ovaries to release eggs.
- Mechanism: Blocks estrogen receptors in the brain, leading to increased production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which promote ovulation.
- Letrozole:
- Purpose: Another medication used to induce ovulation.
- Mechanism: Inhibits estrogen production, leading to increased FSH production and subsequent ovulation.
2. Gonadotropins (FSH and LH):
- Purpose: Used in more complex fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intrauterine insemination (IUI).
- Mechanism: Injectable hormones directly stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
3. Intrauterine Insemination (IUI):
- Purpose: Facilitates the meeting of sperm and egg by placing specially prepared sperm directly into the uterus.
- Procedure: Involves monitoring the woman’s menstrual cycle and timing the insemination to coincide with ovulation.
4. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF):
- Purpose: A more advanced fertility treatment that involves fertilizing an egg with sperm outside the body.
- Procedure:
- Stimulation: Ovaries are stimulated with gonadotropins to produce multiple eggs.
- Retrieval: Eggs are retrieved from the ovaries.
- Fertilization: Eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory.
- Embryo Transfer: Selected embryos are transferred into the uterus.
5. Surgery – Ovarian Drilling:
- Purpose: A surgical option used in some cases to induce ovulation.
- Procedure: Small holes are made in the surface of the ovaries using laser or diathermy, potentially reducing androgen levels and promoting regular ovulation.
Psychological Support
These conditions can impact various aspects of an individual’s life, including emotional well-being, body image, and self-esteem. Providing psychological support is essential to help individuals cope with the challenges and emotional stress associated with PCOD/PCOS. Here are the key components of psychological support:
1. Counseling and Therapy:
- Individual Counseling: One-on-one sessions with a mental health professional can provide a safe space to explore emotions, fears, and coping strategies related to PCOD/PCOS.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns, promoting a more positive mindset.
2. Support Groups:
- Online or In-Person Support Groups: Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide a sense of community and understanding.
- Facilitated Group Sessions: Led by mental health professionals, these sessions allow individuals to share experiences, ask questions, and receive support in a group setting.
Alternative Therapies
While not a substitute for medical treatment, some individuals find relief from symptoms through these alternative methods. Here are short points on alternative therapies:
- Acupuncture: Traditional Chinese practice involves the insertion of thin needles at specific points. Some studies suggest acupuncture may regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels.
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs, such as spearmint and chasteberry, are believed to have potential benefits for hormonal balance. Consult a professional before incorporating herbal supplements.
- Yoga: The mind-body practice involves physical postures, breath control, and meditation. Yoga may help reduce stress, improve hormonal balance, and enhance overall well-being.
- Meditation: Mindfulness meditation and relaxation techniques can reduce stress and support emotional well-being. Incorporating meditation into a daily routine may positively impact hormonal regulation.
- Dietary Changes: Some individuals explore gluten-free or dairy-free diets, emphasizing whole foods. Take dietary changes with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional or nutritionist.
- Aromatherapy: Use of essential oils for relaxation and stress reduction. While aromatherapy may promote a sense of well-being, its impact on PCOD/PCOS is not well-established.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of treatments can vary among individuals, and a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach is often recommended.
How To Get Treatment for PCOD and PCOS?

Getting treatment for Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) involves a systematic approach that typically includes medical consultation, diagnostic assessments, and the development of a personalized treatment plan. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to get treatment for PCOD and PCOS:
1. Consult a Healthcare Professional:
- Schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider, preferably a gynecologist or an endocrinologist, who specializes in women’s health and hormonal disorders.
2. Medical History and Physical Examination:
- Provide a detailed medical history, including menstrual patterns, symptoms, and any relevant family history.
- Undergo a physical examination to assess signs such as hirsutism, acne, and abdominal tenderness.
3. Diagnostic Tests:
- Blood Tests: Measure hormone levels, including FSH, LH, testosterone, and insulin.
- Ultrasound: Conduct a pelvic ultrasound to visualize the ovaries and assess for cysts or other abnormalities.
- Additional Tests: Depending on symptoms, additional tests may be recommended to assess metabolic health, thyroid function, and more.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the treatment landscape for PCOD and PCOS is multifaceted, encompassing lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and emotional well-being. By adopting a holistic approach that addresses the root causes and symptoms, women can better navigate the challenges posed by these conditions.
Seeking personalized medical advice and maintaining a proactive stance towards health can empower individuals to manage PCOD and PCOS effectively, promoting overall well-being and reproductive health.
If you are facing PCOS-related issues, PCOS treatment at HerMantra can help. Book your free trial online Pcos treatment session now.