Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex endocrine disorder that affects millions of women worldwide. Characterized by hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual cycles, and the presence of cysts on the ovaries, PCOS can have a profound impact on a woman’s reproductive health and overall well-being. Timely and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life. In this blog, we’ll delve into the various aspects of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Diagnosis, from recognizing symptoms to undergoing diagnostic tests.
Contents
Understanding PCOS Symptoms
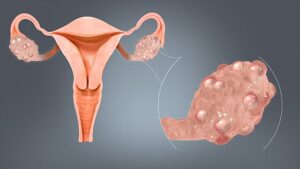
PCOS presents with a myriad of symptoms, and the manifestation varies from woman to woman. To aid in the diagnosis, it’s essential to be aware of the common signs associated with this syndrome:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: One of the hallmark signs of PCOS is irregular periods. Women with PCOS often experience infrequent or prolonged menstrual cycles, which may be accompanied by heavy or scanty bleeding.
- Hyperandrogenism: Elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) can lead to symptoms such as acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and male-pattern baldness.
- Ovulatory Dysfunction: PCOS can disrupt the normal ovulation process, leading to fertility issues and difficulties in conceiving.
- Polycystic Ovaries: As the name suggests, the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries is a key characteristic of PCOS. However, not all women with PCOS have polycystic ovaries, and not all women with polycystic ovaries have PCOS.
Diagnostic Criteria for PCOS Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is typically based on a combination of clinical, laboratory, and imaging criteria. The most widely used criteria for diagnosing PCOS are known as the Rotterdam criteria, which were established in 2003 during a conference in Rotterdam, Netherlands. According to these criteria, a woman may be diagnosed with PCOS if she meets at least two out of three of the following conditions:
- Oligo-ovulation or Anovulation: This refers to irregular or absent menstrual cycles, indicating that ovulation is not occurring regularly. Oligo-ovulation is defined as fewer than eight menstrual cycles per year, while anovulation is the absence of ovulation.
- Clinical and/or Biochemical Signs of Hyperandrogenism: Hyperandrogenism refers to elevated levels of androgens, which are male hormones. Clinical signs include hirsutism (excessive hair growth in areas where men typically grow hair, such as the face, chest, and back), acne, and male-pattern baldness. Biochemical evidence of hyperandrogenism can be confirmed through blood tests that measure elevated levels of androgens such as testosterone.
- Polycystic Ovaries on Ultrasound: The presence of polycystic ovaries is typically confirmed through transvaginal ultrasound. Furthermore, polycystic ovaries are characterized by the presence of multiple small follicles or cysts around the periphery of the ovary. It’s important to note that not all women with PCOS have polycystic ovaries, and the ultrasound findings alone are not sufficient for a PCOS diagnosis.
It’s crucial to consider other conditions that may mimic PCOS symptoms, such as thyroid disorders, hyperprolactinemia, and non-classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Additionally, the diagnostic process may involve ruling out other potential causes of irregular menstrual cycles and androgen excess.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Diagnosis Tests
The diagnosis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history assessment, and specific tests to confirm the presence of characteristic features.
Here are the key diagnostic tests commonly used in the evaluation of PCOS:
Medical History and Physical Examination
- A detailed medical history helps the healthcare provider understand the patient’s menstrual history, symptoms, and potential risk factors.
- A physical examination may include assessing signs of hyperandrogenism, such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth), acne, and male-pattern baldness.
Blood Tests
- Hormone Levels: Blood tests are conducted to measure hormone levels, including:
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Testosterone (total and free)
- Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG)
- Prolactin
- Estradiol
- Insulin Levels: Elevated insulin levels may be associated with insulin resistance, which is common in PCOS. Fasting insulin levels or glucose tolerance tests may be ordered.
Ultrasound Imaging
This imaging technique is used to visualize the ovaries. In PCOS, multiple small follicles may be observed around the periphery of the ovaries, giving them a characteristic appearance often described as “polycystic.” It’s important to note that the presence of polycystic ovaries alone is not sufficient for a PCOS diagnosis; it must be considered alongside other criteria.
Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) Test
The Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) test has emerged as a valuable tool in assessing ovarian function and, in certain contexts, aiding in the evaluation of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Produced by small ovarian follicles, AMH levels are indicative of ovarian reserve, providing insights into the quantity of eggs remaining in a woman’s ovaries. Notably, elevated AMH levels are commonly associated with PCOS due to increased follicular activity, although it is not a standalone diagnostic criterion.
The testing procedure involves a simple blood draw, and its flexibility in timing, not being significantly influenced by menstrual cycles, adds to its convenience. In the realm of fertility treatments, AMH levels are utilized to predict ovarian response during in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedures. While the AMH test is not part of the formal PCOS diagnostic criteria, it contributes valuable information when considered alongside other clinical and laboratory findings, making it an integral component of comprehensive reproductive health assessment.
Thyroid Function Tests
Thyroid function tests are essential tools in evaluating the health of the thyroid gland, a critical regulator of metabolism and hormonal balance. These tests help assess the production of thyroid hormones, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), and the functioning of the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland. Elevated or reduced levels of these hormones can indicate thyroid dysfunction.
The primary thyroid function test, TSH, reflects the feedback mechanism controlling thyroid hormone production. Furthermore, abnormal TSH levels may prompt additional tests to measure T4 and T3 to pinpoint the specific thyroid disorder.
Thyroid function tests are crucial in identifying conditions such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, both of which can present with symptoms mimicking those of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Including thyroid assessments in the diagnostic process helps rule out thyroid-related causes of irregular menstrual cycles, androgen excess, and fertility issues, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of reproductive health.
Pelvic Laparoscopy (In Some Cases)
Pelvic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that may be recommended in certain cases to aid in the diagnosis and management of various gynecological conditions, including Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). While it is not a routine diagnostic tool for PCOS, it can be considered when other diagnostic methods are inconclusive or when additional information is needed.
During pelvic laparoscopy, a small incision is made near the navel, and a thin, lighted instrument called a laparoscope is inserted to visualize the pelvic organs, including the ovaries. This allows for direct examination of the ovaries, assessment of their size, and identification of any abnormalities. Pelvic laparoscopy can provide valuable information about the presence of cysts, adhesions, or other structural issues that may contribute to symptoms associated with PCOS.
How To Get Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Diagnosis?

Getting a Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) diagnosis involves a collaborative effort between you and your healthcare provider. If you suspect you have PCOS or are experiencing symptoms associated with the syndrome, here is a step-by-step guide on how to proceed:
- Schedule an Appointment: Reach out to your primary care physician, gynecologist, or endocrinologist to schedule an appointment. Furthermore, if you don’t have a primary care provider, you may consider seeking care from a women’s health specialist.
- Prepare for the Appointment: Provide information about your medical history, including any relevant family history of hormonal or reproductive issues. Make a list of your symptoms, including details about your menstrual cycles, any signs of hyperandrogenism (such as acne or hirsutism), and any concerns related to fertility.
- Discussing Results: Once the test results are available, your healthcare provider will discuss the findings with you. Based on the Rotterdam criteria, a PCOS diagnosis is made if you meet at least two out of three criteria related to oligo-ovulation/anovulation, hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovaries.
- Developing a Treatment Plan: If diagnosed with PCOS, your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan. Treatment may involve lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, hormonal contraceptives to regulate menstrual cycles, and medications to address specific symptoms.
Conclusion
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a multifaceted condition that requires careful evaluation and diagnosis. By being aware of the symptoms and seeking timely medical advice, women can take proactive steps towards managing their health and improving their quality of life.
A collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers is essential for effective diagnosis and the development of personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual’s unique needs.
If you are facing PCOS-related issues, PCOS treatment at HerMantra can help. Book your free trial online Pcos treatment session now.


