Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex endocrine disorder that affects many women worldwide. One variant of PCOS that often poses unique challenges is characterized by elevated levels of luteinizing hormone (LH), commonly known as high LH PCOS. This form of PCOS requires a targeted and nuanced approach to treatment, taking into account the hormonal imbalances that set it apart from other PCOS subtypes. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of high LH PCOS and explore effective treatment strategies to help women regain hormonal balance and improve their overall health.
Contents
What is High LH PCOS?
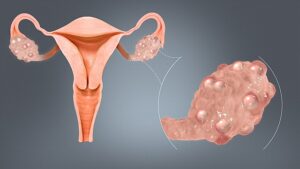
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder that affects people assigned to females at birth, often during their reproductive years. PCOS is characterized by a combination of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, ovarian cysts, and hormonal imbalances. There are different subtypes or phenotypes of PCOS, and one specific variant is characterized by elevated levels of luteinizing hormone (LH), known as high LH PCOS.
Luteinizing hormone (LH) is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, and it plays a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and ovulation. In a typical menstrual cycle, the levels of LH and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) rise and fall in a coordinated manner to facilitate the release of an egg from the ovary (ovulation).
There is an imbalance in the LH and FSH levels in high LH PCOS. Normally, FSH is responsible for stimulating the growth of ovarian follicles, and a surge in LH triggers ovulation. However, in high LH PCOS, the elevated levels of LH may disrupt this delicate balance. This hormonal imbalance can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, anovulation (lack of ovulation), and fertility issues.
The specific causes of high LH PCOS are not fully understood, and the condition likely involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. High LH levels are often associated with an overproduction of androgens (male hormones), contributing to symptoms such as acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and other manifestations of hyperandrogenism.
It’s important to note that PCOS is a heterogeneous condition, meaning its presentation can vary among individuals. Some people with PCOS may have high LH levels, while others may have normal or low levels. Therefore, a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, including blood tests and a comprehensive medical history, is essential to diagnose and determine an individual’s specific characteristics of PCOS.